Big data is data in the order of terabytes or petabytes and beyond, consisting of mining, analysis, and predictive modeling of large datasets. The rapid growth of information and technological developments has provided a unique opportunity for individuals and enterprises across the world to derive profits and develop new capabilities redefining traditional business models using large-scale analytics.
This article provides a bird's eye view on five of the most popular open source data platforms. Here's our list:
Apache Hadoop
Apache Hadoop is an open source software platform that processes very large datasets in a distributed environment with respect to storage and computational power, and is mainly built on low cost commodity hardware.
Apache Hadoop is designed to easily scale up from a few to thousands of servers. It helps you to process locally stored data in an overall parallel processing setup. One of the benefits of Hadoop is that it handles failure at a software level. The following figure illustrates the overall architecture of the Hadoop Ecosystem and where the different frameworks are within it:
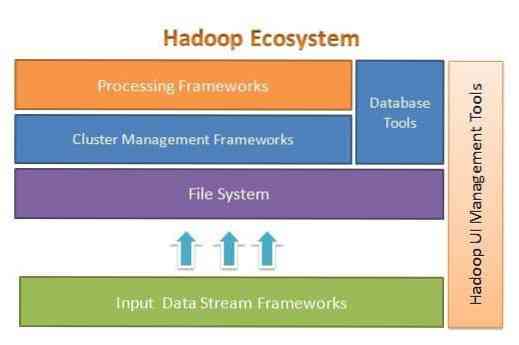
Apache Hadoop provides a framework for the file system layer, cluster management layer, and the processing layer. It leaves an option for other projects and frameworks to come and work alongside Hadoop Ecosystem and develop their own framework for any of the layers available in the system.
Apache Hadoop is comprised of four main modules. These modules are Hadoop Distributed File System (the file system layer), Hadoop MapReduce (which works with both cluster management and the processing layer), Yet Another Resource Negotiator (YARN, the cluster management layer), and Hadoop Common.
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is a full text-based search and analytics engine. It is a highly scalable and distributed system, specifically designed to work efficiently and quickly with big data systems, where one of its main use cases is log analysis. It is capable of performing advanced and complex searches, and almost real-time processing for advanced analytics and operational intelligence.
Elasticsearch is written in Java and is based on Apache Lucene. Released in 2010 and it quickly gained popularity because of its flexible data structure, scalable architecture, and very fast response time. Elasticsearch is based on a JSON document with a schema-free structure, making adoption easy and hassle-free. It is one of the top-ranking search engines of enterprise grade. You can write its client in any programming language; Elasticsearch officially works with Java, .NET, PHP, Python, Perl, and so on.
Elasticsearch mainly interacts using a REST API. It gets data in the form of JSON documents with all of the required parameters, and provides its response in a similar fashion.
MongoDB
MongoDB is a NoSQL database based on the document store data model. In MongoDB everything is either collection or document. In order to understand MongoDB terminology, collection is an alternate word for table, whereas document is an alternate word for rows.
MongoDB is an open source, document-oriented, and cross-platform database. It is primarily written in C++. It is also the leading NoSQL database that provides high performance, high availability, and easy scalability. MongoDB uses JSON-like documents with schema and provides a rich query support. Some of it prime features include indexing, replication, load balancing, aggregation, and file storage.
Cassandra
Cassandra is an open source Apache Project designed for NoSQL database management. Cassandra rows are organized into tables and indexed by a key. It uses an append-only, log-based storage engine. Data in Cassandra is distributed across multiple masterless nodes, with no single point of failure. It is a top-level Apache project, and its development is currently overseen by the Apache Software Foundation (ASF).
Cassandra is designed to solve problems associated with operating at a large (web) scale. Given Cassandra's masterless architecture, it is able to continue to perform operations despite a small (albeit significant) number of hardware failures. Cassandra runs across multiple nodes across multiple data centers. It replicates data across these data centers to avoid failure or downtime. This makes it a highly fault-tolerant system.
Cassandra uses its own programming language to access data across its nodes. It is called Cassandra Query Language or CQL. It is similar to SQL, which is mainly used by Relational Databases. CQL can be used by running its own application called cqlsh. Cassandra also provides many integration interfaces for multiple programming languages to build an application using Cassandra. Its integration API supports Java, C++, Python, and others.
Apache HBase
HBase is another Apache Project designed to manage the NoSQL data store. It is designed to make use of Hadoop Ecosystem's features, including reliability, fault tolerance, and so on. It utilizes HDFS as a file system for storage purposes. There are multiple data models that NoSQL works with and Apache HBase belongs to the column-oriented data model. HBase was originally based on Google Big Table, which is also related to the column-oriented model for unstructured data.
HBase stores everything in the form of a key-value pair. The important thing to note is that in HBase, a key and a value are in the form of bytes. So, to store any information in HBase, you have to convert information into bytes. (In other words, its API doesn't accept anything other than byte array.) Be careful with HBase, as when you store data, you should remember its original type. Data that was originally a string will return as a byte array if recalled incorrectly. As a result, it will create a bug in your application and crashes your application.
Hope you enjoyed this article. If you are looking to architect and design data-intensive applications, then you can explore Anuj Kumar's Architecting Data-Intensive Applications. This book is your gateway to build smart data-intensive systems by incorporating the core data-intensive architectural principles, patterns, and techniques directly into your application architecture.
 Phenquestions
Phenquestions